What are the FastBridge Assessments?
FastBridge Assessments are computer-adaptive tests used by schools to evaluate student progress in reading, math, and social-emotional behavior from Kindergarten through Grade 12. The two most common FastBridge tests are aReading (reading) and aMath (math).
Keep reading to try free sample questions.
Prepare for Success on the FastBridge Assessment
The FastBridge assessment helps schools track student progress in reading and math across K–12. These tests are adaptive—meaning question difficulty changes based on how your child answers—and they align with Common Core State Standards.
If you’re a parent searching for FastBridge assessment resources for parents, you’ve come to the right place.
Shop All PrepPacks
Get full-length practice test with detailed explanations and proven study strategies.
Sample FastBridge aReading Questions – 2nd & 3rd Grade
The FastBridge Reading assessment is called aReading. The test consists of 30-60 questions and has no time constraint, although it typically takes about 30-45 minutes to complete.
FastBridge Reading Assessment -2nd Grade Questions
Here are sample questions to assess Fastbridge aReading skills for 2nd grade students. These questions focus on foundational skills.
Question 1: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
Which word starts with the sound of the letters s and h together (sh)?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I picked "shop" because it starts with the "sh" blend, just like in "shoes" or "shark." Listening for these sound chunks helps build strong phonics skills.
Try practicing "sh" words by saying them out loud and spotting them in storybooks. The more you hear it, the easier it gets."
Question 2: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
How many syllables does the word umbrella have?
Question 3: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
Which of the following words has a silent letter
Question 4: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
Which is a complete sentence?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Here’s how I explain complete sentences to my students:
A complete sentence is like a finished thought – it tells a whole idea from start to end. I always remind my students that a good sentence has three must-haves: it starts with a capital letter, it has a subject (who or what we're talking about), and a verb (what that person or thing is doing). Just as important, it ends with the right punctuation – a period (.), a question mark (?), or an exclamation point (!)."
-
The dog barks.
-
Subject: "The dog" (who the sentence is about).
-
Verb: "barks" (what the dog does).
-
-
Emma runs fast.
-
Subject: "Emma" (who the sentence is about).
-
Verb: "runs" (what Emma does).
-
Sometimes, sentences also have an object. The object is the thing that the action happens to.
-
Jake kicks the ball.
-
Subject: "Jake" (who kicks).
-
Verb: "kicks" (the action).
-
Object: "the ball" (what Jake kicks).
-
What About Questions?
Questions are also sentences! For example:
-
What is your name?
-
Subject: "your name" (what the sentence is about).
-
Verb: "is" (the action).
-
How to Check If Your Sentence is Complete:
-
Does it have a subject? (Who or what is the sentence about?)
-
Does it have a verb? (What is the subject doing or being?)
-
Does it make sense by itself?
If the answer is yes to all three, you’ve written a complete sentence!
Question 5: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
In which sentence is the underlined word spelled correctly?
Question 6: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
Noodles have a long history! Some of the oldest noodles were found in China and are over 4,000 years old. People in many different countries have enjoyed eating noodles for centuries. Noodles are made from dough and can be cooked in lots of ways, like boiling or frying.
What is the passage mainly about?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"When I teach my students how to find the main idea, I always tell them to ask themselves one simple question: "What is this whole passage mostly about?" Not just one sentence or detail—but the big picture.
Remember: when finding the main idea, don’t get tricked by interesting facts or details. Always look at what the whole passage is trying to teach you. That’s your main idea!"
Question 7: FastBridge Reading 2nd Grade
The field was a sea of golden grass, waving gently in the soft breeze. Long shadows stretched out from the old oak tree at the edge, reaching almost to the little stream that gurgled nearby. The sun was sinking lower in the sky, painting the clouds with splashes of orange and pink. Bumblebees buzzed lazily among the wildflowers, and a few crickets began their chirping song.
What time of day is it?
FastBridge Reading Assessment -3rd Grade Questions
Let's look at some sample questions for the FastBridge Reading Assessment for 3rd grade.
Before diving into these examples, it can be helpful for students to warm up with some targeted reading exercises for 3rd grade. This can help reinforce key concepts and build confidence before tackling assessment-style questions.
Question 8: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
Which words have a short vowel sound? Click all the answers that are correct
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Here's a great tutor tip I always share with my students: Knowing the difference between long and short vowels can really boost your reading and spelling skills. When you understand how vowel sounds work, it becomes easier to pronounce words correctly and recognize common spelling patterns.
Practice saying the words out loud, listening closely to the vowel sounds."
| Short A |
| -at: cat, bat, hat, mat, pat, rat, sat, fat |
| -an: can, fan, man, pan, ran, tan, van |
| -ag: bag, gag, lag, nag, rag, tag, wag |
| -ap: cap, gap, lap, map, nap, rap, sap, tap |
| -ad: bad, dad, had, lad, mad, pad, sad |
| -am: ham, jam, ram, yam |
| Short E |
| -et: bet, get, jet, let, met, net, pet, set, wet |
| -en: den, hen, men, pen, ten |
| -ed: bed, fed, led, red, wed |
| Short I |
| -it: bit, fit, hit, kit, lit, pit, sit |
| -in: bin, fin, pin, tin, win |
| -ig: big, dig, fig, pig, rig, wig |
| -ip: dip, hip, lip, nip, rip, sip, tip, zip |
| -id: bid, hid, kid, lid, rid |
| Short O |
| -ot: cot, dot, got, hot, lot, not, pot, rot |
| -op: hop, mop, pop, top |
| -og: dog, fog, hog, log |
| -ob: cob, job, mob, rob, sob |
| -ox: box, fox |
| Short U |
| -ut: cut, gut, hut, nut, rut |
| -un: bun, fun, gun, run, sun |
| -ug: bug, dug, hug, jug, mug, rug, tug |
| Long A (sounds like /ā/ as in "cake") |
| a_e: cake, bake, make, take, late, date, gate, rate |
| ai: rain, train, pain, wait, sail, mail, chain |
| ay: day, play, say, way, stay, may, pay |
| ea: break, steak (sometimes) |
| Long E (sounds like /ē/ as in "tree") |
| ee: tree, see, bee, feel, meet, week, sleep, keep |
| ea: eat, sea, read, meat, beat, seat, team, dream |
| ie: piece, field, believe |
| y: baby, happy, funny, party, sunny, city, very (at the end of words) |
| e_e: these, these, eve |
| Long I (sounds like /ī/ as in "bike") |
| i_e: bike, like, time, fine, mine, ride, side, wide |
| ie: pie, tie, lie, die |
| igh: high, light, night, right, sight |
| y: cry, fly, sky, try, my |
| Long O (sounds like /ō/ as in "boat") |
| o_e: bone, home, rope, nose, rose, code, note, vote |
| oa: boat, coat, road, soap, toast |
| ow: snow, grow, low, show, bowl |
| Long U (has two main sounds) |
| /ū/ as in "cube" (sometimes called "long u 1") |
| u_e: cube, tube, cute, mute, fuse, huge |
| ew: few, new |
| /oo/ as in "moon" (sometimes called "long u 2") |
| oo: moon, soon, food, pool, room |
| ue: blue, true |
Question 9: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
Which of the following words does not rhyme with the word "puff"?
Question 10: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
Which of the following are opposites of " wonderful "?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"When I'm helping students understand vocabulary, I always remind them to look for clues in the meaning of the word. For example, the word "friend" describes someone who is kind, supportive, or someone you like to spend time with. So, when a question asks for the opposite of "friend," I ask myself, "What word would describe someone who is mean, hurtful, or someone you don't trust?"
Words like "enemy" or "foe" are strong opposites of "friend" because they describe people who are against you or not supportive. But words like "buddy" and "pal" actually mean the same thing as "friend," so they aren't opposites at all!
A great tip is this: If you're not sure, try using the word in a sentence and then switch it out. For example: "She is my best friend." Now try: "She is my worst enemy." That changes the meaning completely—which means you found an opposite!"
Question 11: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
Choose the word that best completes the sentence:
The____________ elephant trumpeted loudly, shaking the ground with each heavy step.
Question 12: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
The Statue of Liberty, a gift from France, stands proudly on Liberty Island. It's also known as "Liberty Enlightening the World," and its green color comes from the copper it's made of. Some people think the Statue of Liberty is one of the most important symbols of freedom in the world.
Which of the following sentences is an opinion?
Question 13: FastBridge Reading 3rd Grade
What literary device is used most in the poem?
Shopping Sounds
Down the aisles with squeaky carts,
Beep! goes each item as checkout starts.
Rustling bags and shuffling feet, Ding!
The register makes receipts complete.
Click-clack goes the drawer with cash inside, Swoosh!
The cards through readers glide.
Crinkle-crunch as bags we fill,
Ka-ching! echoes from the till.
Boost Reading Fluency and Comprehension!
Our 2nd and 3rd Grade FastBridge Reading Prep Packs make learning fun and effective
Sample FastBridge aMath Questions – 2nd & 3rd Grade
The FastBridge Math assessment is called aMath. The test measures broad mathematics skills. The Math assessment typically consists of 30-60 questions and takes approximately 20-30 minutes to finish, but it has no time limit.
FastBridge Math Assessment -2nd Grade Questions
Question 1: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
What number is missing from the following equation?
15 + ___ = 24
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"When I work with 2nd graders, I love teaching them about inverse operations because it makes math click! Inverse operations are math actions that undo each other. Addition and subtraction are a great example.
I always explain that if you know 9 + 4 = 13, you can check your answer by doing the opposite: 13 - 4 = 9. Or you can check it the other way: 13 - 9 = 4. I tell my students, "If you’re not sure, try the other way!"
Question 2: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
Round 63 to the nearest ten.
Question 3: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
What is 369,482 written in expanded form?
Choose the correct answer:
Question 4: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
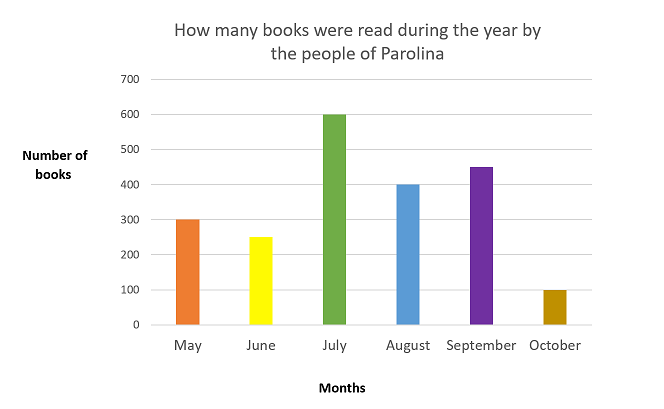
How many books were read in the month of August?
Question 5: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
Question: How many minutes are in 2 ½ hours?
Question 6: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
Which statement is true for every rectangle?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I want to share a little tip with you: Geometry is absolutely fascinating because it's all about shapes, sizes, and how we can use them in the world around us. In this guide, I'll walk you through the rules and properties of both 2D (flat) shapes and 3D (solid) shapes. Let’s get started!"
2D shapes are flat and only have two dimensions: length and width. Here are the most common 2D shapes and their properties:
1. Circle
-
No sides or corners.
-
Every point on the edge is the same distance from the center.
-
Examples: clock face, pizza.
2. Square
-
4 equal sides.
-
4 corners (right angles).
-
Opposite sides are parallel.
-
Examples: checkerboard squares, tiles.
3. Rectangle
-
4 sides (opposite sides are equal).
-
4 corners (right angles).
-
Opposite sides are parallel.
-
Examples: doors, books.
4. Triangle
-
3 sides.
-
3 corners.
-
Can have different types: equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), or scalene (no sides equal).
-
Examples: traffic signs, slices of pie.
5. Hexagon
-
6 sides.
-
6 corners.
-
Examples: honeycombs, nuts and bolts.
6. Pentagon
-
5 sides.
-
5 corners.
-
Examples: soccer ball patterns, The Pentagon building.
Rules for 2D Shapes:
-
Add up all the corners to check the total degrees. For example:
-
A triangle always adds up to 180°.
-
A square or rectangle always adds up to 360°.
-
A pentagon adds up to 540°.
-
A hexagon adds up to 720°.
-
-
Opposite sides in a rectangle or square are always parallel.
-
In parallelograms (like squares, rectangles, and rhombuses):
-
Opposite sides are always parallel and equal in length.
-
Angles opposite each other are always equal.
-
Adjacent angles add up to 180°.
-
-
In trapezoids, only one pair of sides is parallel.
-
Parallel lines stay the same distance apart and never meet, no matter how far they are extended.
3D shapes have three dimensions: length, width, and height. They are not flat and can hold things inside.
1. Cube
-
6 faces, all squares.
-
12 edges and 8 corners.
-
Examples: dice, boxes.
2. Rectangular Prism
-
6 faces, all rectangles (or squares).
-
12 edges and 8 corners.
-
Examples: cereal boxes, bricks.
3. Sphere
-
No faces, edges, or corners.
-
Perfectly round.
-
Examples: balls, oranges.
4. Cylinder
-
2 circular faces (top and bottom).
-
1 curved surface.
-
Examples: cans, drums.
5. Cone
-
1 circular face (base).
-
1 curved surface.
-
Comes to a point (vertex).
-
Examples: ice cream cones, traffic cones.
6. Pyramid
-
1 base (can be a square, triangle, or other shape).
-
Triangular faces that meet at a point (vertex).
-
Examples: Egyptian pyramids, tent shapes.
Rules for 3D Shapes:
-
Faces are the flat surfaces.
-
Edges are where two faces meet.
-
Corners (or vertices) are where edges meet.
Question 7: FastBridge Math 2nd Grade
Question: What is the perimeter of a regular hexagon whose side measures 8 cm?
FastBridge Math Assessment -3rd Grade Questions
Question 8: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
A train left the station with 85 passengers. At the first stop, 32 passengers got on the train, and 17 passengers got off. How many passengers are now on the train?
Question 9: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
Identify the equations that are equal to 450. Select all the correct options.
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"As your expert math tutor, I'm here to guide you through some essential math skills! We'll cover addition, multiplication, subtraction, the order of operations, and comparing expressions. Mastering these will make solving problems, like identifying which equations equal 360, a breeze."
1. Addition of Multiples of 10
Adding multiples of 10 is simple! Just focus on the tens place.
Example: 300 + 60
-
Add the tens: 30 + 6 = 36.
-
Now add the zeros back: 300 + 60 = 360.
Tip: Always line up the numbers by their place values.
2. Multiplication
Multiplication means repeated addition. To solve problems, multiply the numbers step by step.
Example: 6 x 60
-
Break it down: 6 x 60 is the same as 6 x (6 x 10).
-
First, multiply: 6 x 6 = 36.
-
Then multiply by 10: 36 x 10 = 360.
Tip: Remember to multiply each digit, then add any zeros at the end.
3. Subtraction
Subtraction means taking away one number from another.
Example: 400 - 40
-
Start with the hundreds: 400.
-
Take away 40: 400 - 40 = 360.
Tip: Line up the numbers by their place values to avoid mistakes.
4. Order of Operations with Parentheses
Parentheses tell you what to solve first. Follow this order:
-
Parentheses
-
Multiplication or Division
-
Addition or Subtraction
Example: (10 x 40) - 40
-
Solve inside the parentheses first: 10 x 40 = 400.
-
Then subtract: 400 - 40 = 360.
Tip: Always complete the operations inside parentheses before moving on.
5. Comparing Expressions to Find Equal Values
To compare expressions, solve each one and see if they match.
Example Question: Identify the equations that are equal to 360. Select all the correct options.
-
A. 300 + 60 = 360
-
B. 6 x 60 = 360
-
C. 400 - 40 = 360
-
D. (10 x 40) - 40 = 360
-
E. (15 x 30) - 90 = 360
How to Solve:
-
Solve each expression step by step.
-
Check if the result equals 360.
Tip: Write down each step to avoid errors.
Practice Time!
Now it’s your turn to practice:
-
Solve 200 + 160.
-
Multiply 8 x 50.
-
Subtract 500 - 140.
-
Solve (12 x 30) - 20.
If you like these tips, read our guide to maths for 3rd graders. You can use them to work on the math sheets for 3rd grade.
Question 10: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
Sienna is organizing a birthday party for 24 people. ¾ of them are vegetarian. How many vegetarian meals does she need to prepare?
Question 11: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
Which of the numbers is not a prime number?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Here's a super-duper tip to help you find out if a number is prime:
You only need to try dividing the number by a few small, special numbers: 2, 3, 5, and 7.
Why these numbers? Because if a number can be divided by anything else, it probably already has one of these smaller numbers as a helper!"
Question 12: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
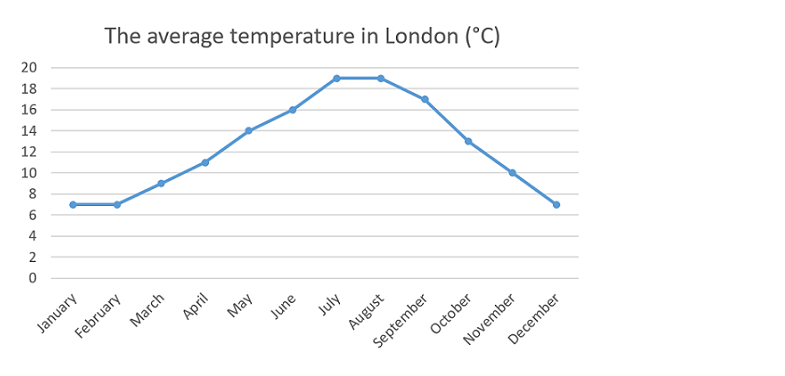
Which pair of months has the largest difference in average temperature in London?
Question 13: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
Maya started to read the newspaper at 2:23 p.m. The reading took her 58 minutes. 11 minutes before she finished reading the newspaper, the phone rang. What time was it when the phone rang?
Question 14: FastBridge Math 3rd Grade
Which of the following triangles is an isosceles triangle?
Turn Math Struggles into Triumphs!
Equip your child with confidence and skill—get our FastBridge Math Prep Pack today
FastBridge Assessment Scores
The FastBridge Assessments uses a scaled score system, for the Math assessments it ranges between 145-275 and for the Reading it’s 350-750.
Understanding FastBridge Scores:
Here's a breakdown of some key points about FastBridge scores:
- Scalability: FastBridge Math and Reading scores are adjusted to ensure they're comparable across different test versions. This means even if the tests have different difficulty levels or structures, you can still compare scores from different versions.
- Adaptive Testing: FastBridge uses adaptive testing, which means the questions get harder or easier based on how the student answers. This helps get a more accurate picture of what the student actually knows.
- Validity and Reliability: FastBridge assessments are reliable and valid for making educational decisions. This means teachers can trust the scores to guide their teaching. Here's how:
- Data-Driven Instruction: Teachers can use FastBridge scores to track student progress and tailor their teaching strategies accordingly.
- Monitoring Progress: FastBridge scores are used for ongoing progress monitoring, allowing teachers to adjust their approach in real-time based on student needs.
- Parent Involvement: Scores can be shared with parents, keeping them informed about their child's progress and fostering their involvement in the educational process.
In short: FastBridge scores provide a valuable framework for evaluating student performance in math and reading. This helps educators make informed decisions to improve learning outcomes and create a dynamic learning environment.
Maximize Assessment Results! Get the ultimate prep for Reading and Math with our FastBridge Test Prep Packs today
How to Prepare for the FastBridge Assessments?
It's great you're looking to prepare for the Fastbridge Assessment! Here's a breakdown of actionable tips based on the skills you listed, combining general test-prep strategies with specific advice for each area:
General Test-Prep Strategies
- Understand the Format: Familiarize yourself with the types of questions and tasks in each section. Fastbridge often uses multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, and fill-in-the-blank formats.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key. Use practice tests, sample questions, and resources provided by your school or online platforms like TestPrep-Online.
- Time Management: Practice working within time limits to get comfortable with the pace of the assessment.
- Get Adequate Rest: Ensure you get enough sleep before the assessment to be alert and focused.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan specific times to focus on each skill area, breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable chunks.
Strengthen Skills Across the Board!
Help your child excel in FastBridge Reading and Math with our expertly designed Prep Packs
FastBridge Learning Strategies
Reading
Foundational Skills:
- Phonics: Practice letter-sound correspondence, blending sounds to form words, and segmenting words into individual sounds.
- Sight Words: Memorize high-frequency words (e.g., "the," "a," "is") to improve reading fluency.
- Concepts of Print: Understand how books work (e.g., reading left to right, top to bottom), identify parts of a book (cover, title page), and recognize punctuation.
Informational Reading:
- Main Idea and Supporting Details: Practice identifying the main idea of a passage and the details that support it.
- Text Features: Pay attention to headings, subheadings, captions, and diagrams to understand the organization and key information in the text.
- Inference: Practice drawing conclusions based on information presented in the text.
Language (Listening and Speaking):
- Active Listening: Practice listening attentively to instructions and information.
- Clear Communication: Practice expressing ideas clearly and concisely.
Reading Literature:
- Story Elements: Understand plot, characters, setting, and theme.
- Figurative Language: Recognize and interpret metaphors, similes, and other figures of speech.
Math
Counting & Cardinality:
- Number Recognition: Practice recognizing and writing numbers.
- Counting Sequence: Practice counting forward and backward, and skip counting.
Operations & Algebraic Thinking:
- Basic Facts: Memorize addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division facts.
- Problem Solving: Practice solving word problems using different strategies.
Number & Operations in Base Ten:
- Place Value: Understand the value of digits in different places (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.).
- Regrouping: Practice regrouping in addition and subtraction.
Number & Operations—Fractions:
- Fraction Concepts: Understand parts of a whole, equivalent fractions, and comparing fractions.
- Operations with Fractions: Practice adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions.
Measurement & Data:
- Measurement Units: Familiarize yourself with different units of measurement (length, weight, time).
- Data Representation: Practice interpreting graphs, charts, and tables.
Geometry:
- Shape Recognition: Identify and classify different shapes.
- Spatial Reasoning: Practice visualizing and manipulating shapes.
- Ratios & Proportional Relationships:
- Ratio Concepts: Understand the concept of ratios and how to express them.
- Proportional Reasoning: Practice solving problems involving proportions.
FAQ’s
For the Reading assessment, the highest score possible is 750 and for the Math assessment, it’s 275.
The aMath and aReading tests are untimed but they take around 20-30 minutes and 30-45 minutes respectively.
Because the tests are adaptive the number of questions varies per student but the number of questions range between 30-60.
They assess reading and math growth across the school year (Fall, Winter, Spring).
A “good” score means meeting or exceeding grade-level benchmarks. Teachers use percentile rankings to guide intervention or enrichment.



